Project SFB622
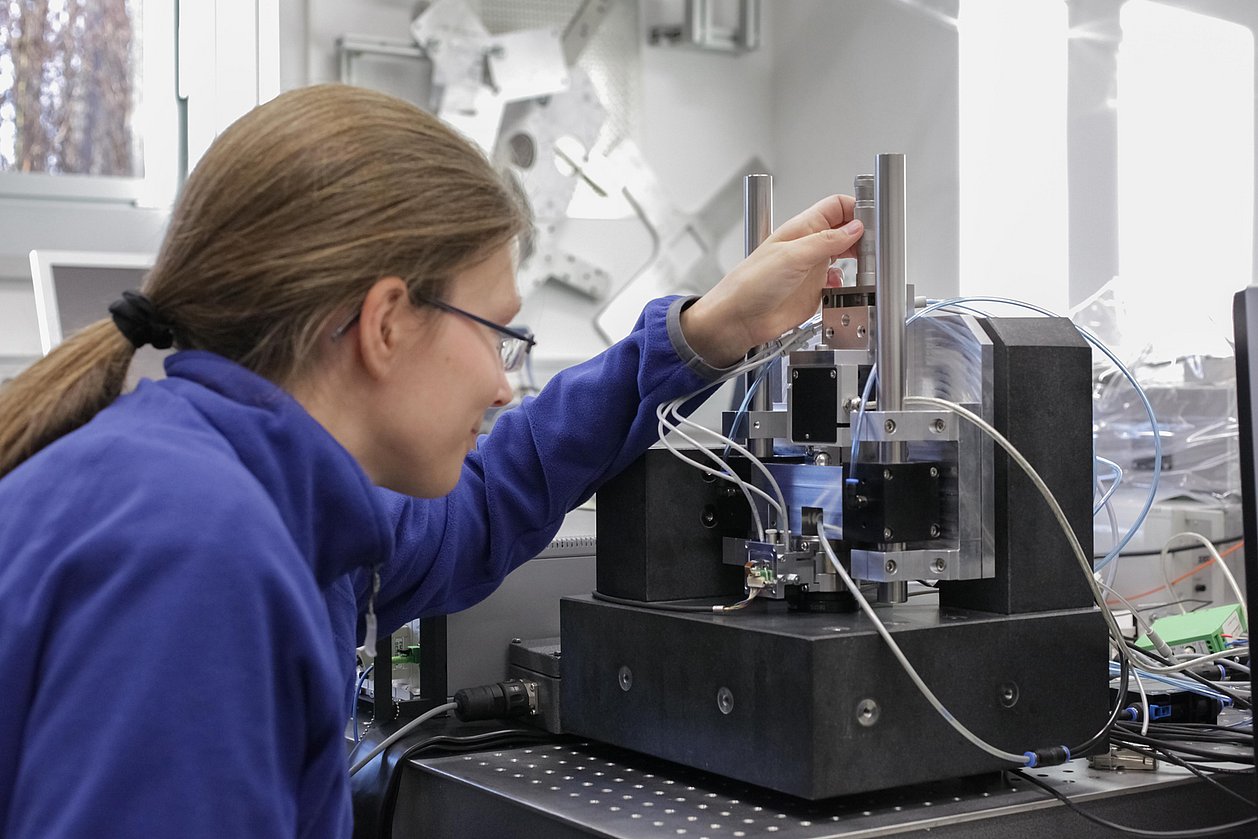
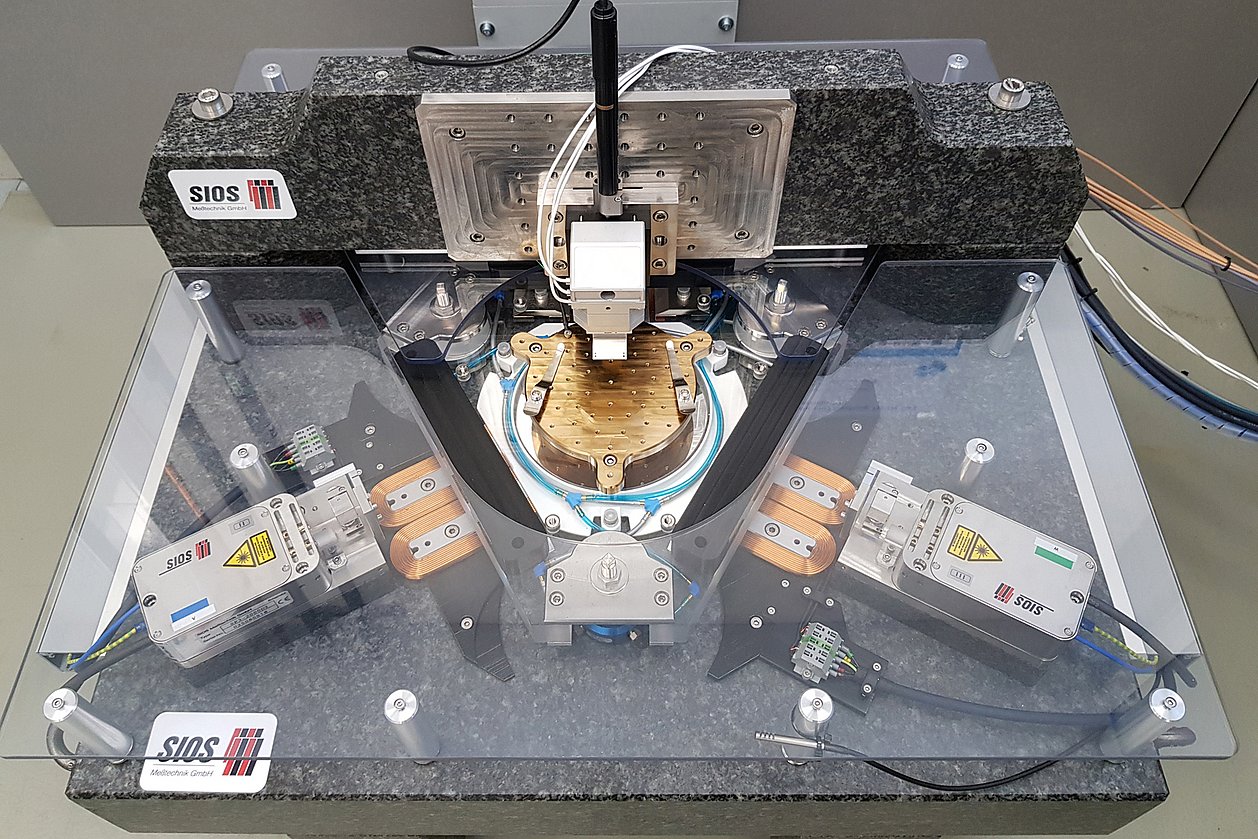
The work of IMMS on novel high-precision drives contributes to nanopositioning systems acting over long distances of travel.
Nanopositioning and nanomeasuring machines (NPMM) blaze the trail and provide the necessary preconditions for the development of nanotechnologies. Without these systems there is no access to the world of nanometres, since NPM machines are indispensable for measuring, positioning, probing, manufacturing and manipulation of objects with nanometer precision. Such a technique is essential for micro- and nanoelectronics, micromechanics and precision engineering, materials research and metrology, optics and molecular biology.
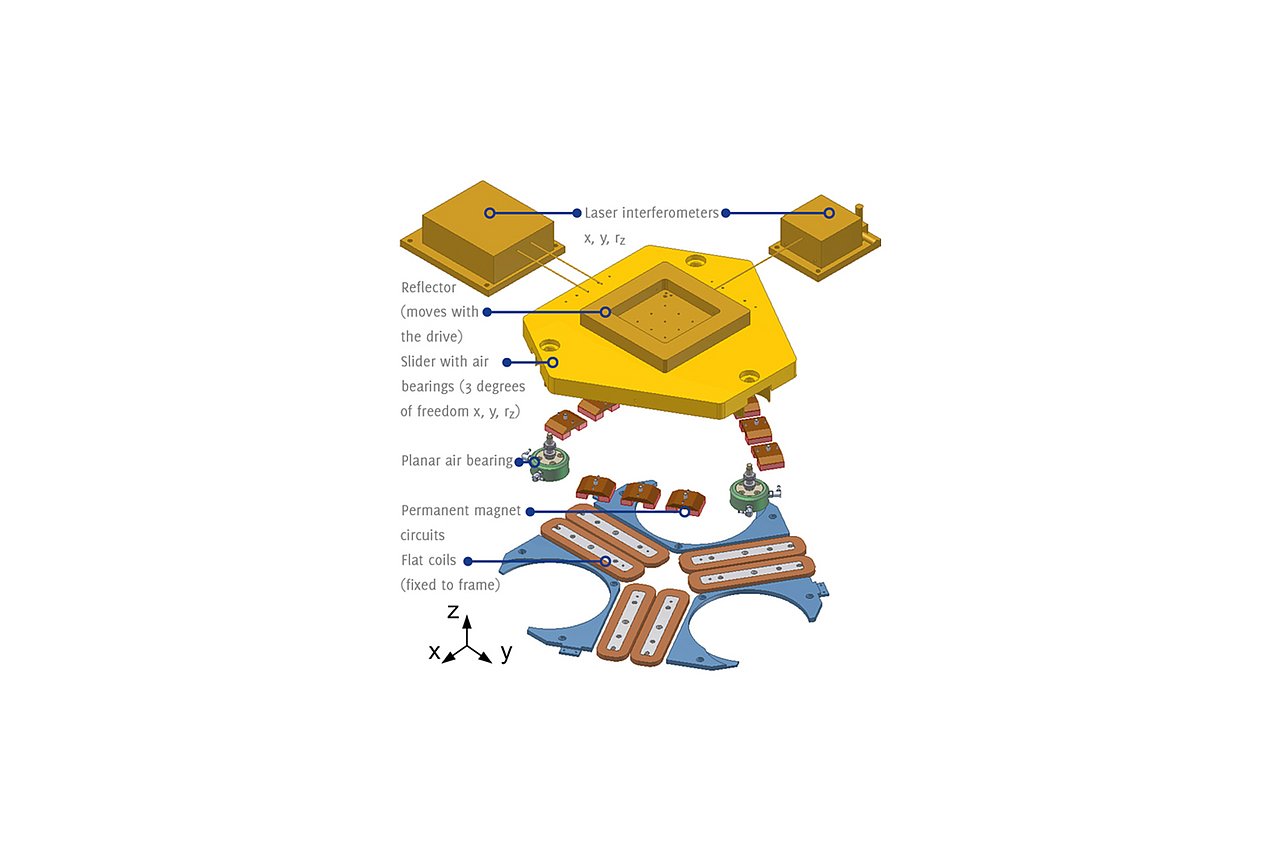
IMMS’ specific and ever-deepening contribution to the research is precision-drive know-how and, above all, expertise in the field of integrated multi-coordinate drives. In the subproject “Nanopositioning Systems for Large Travel Ranges” the Institute worked on novel high-precision drives and high-performance controls for nanopositioning systems acting over long distances of travel.
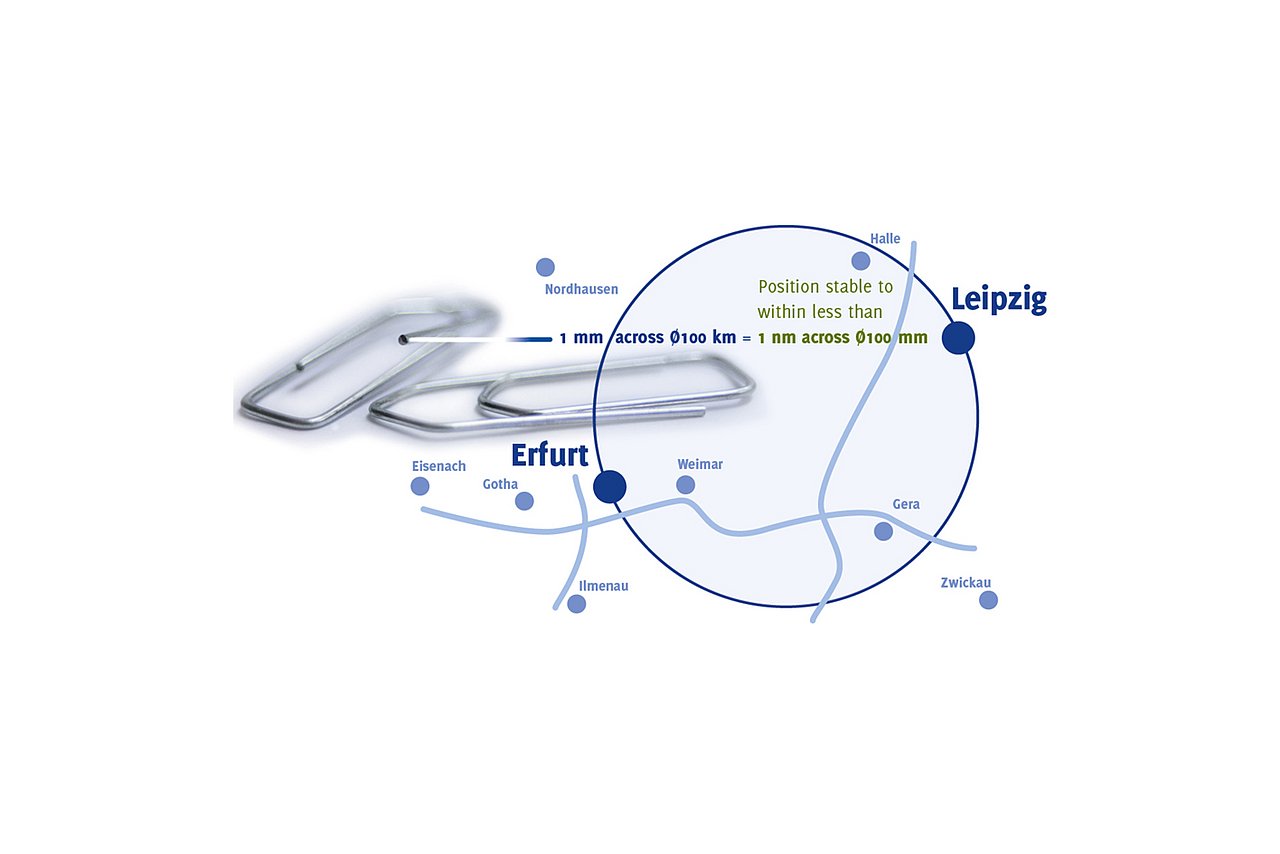
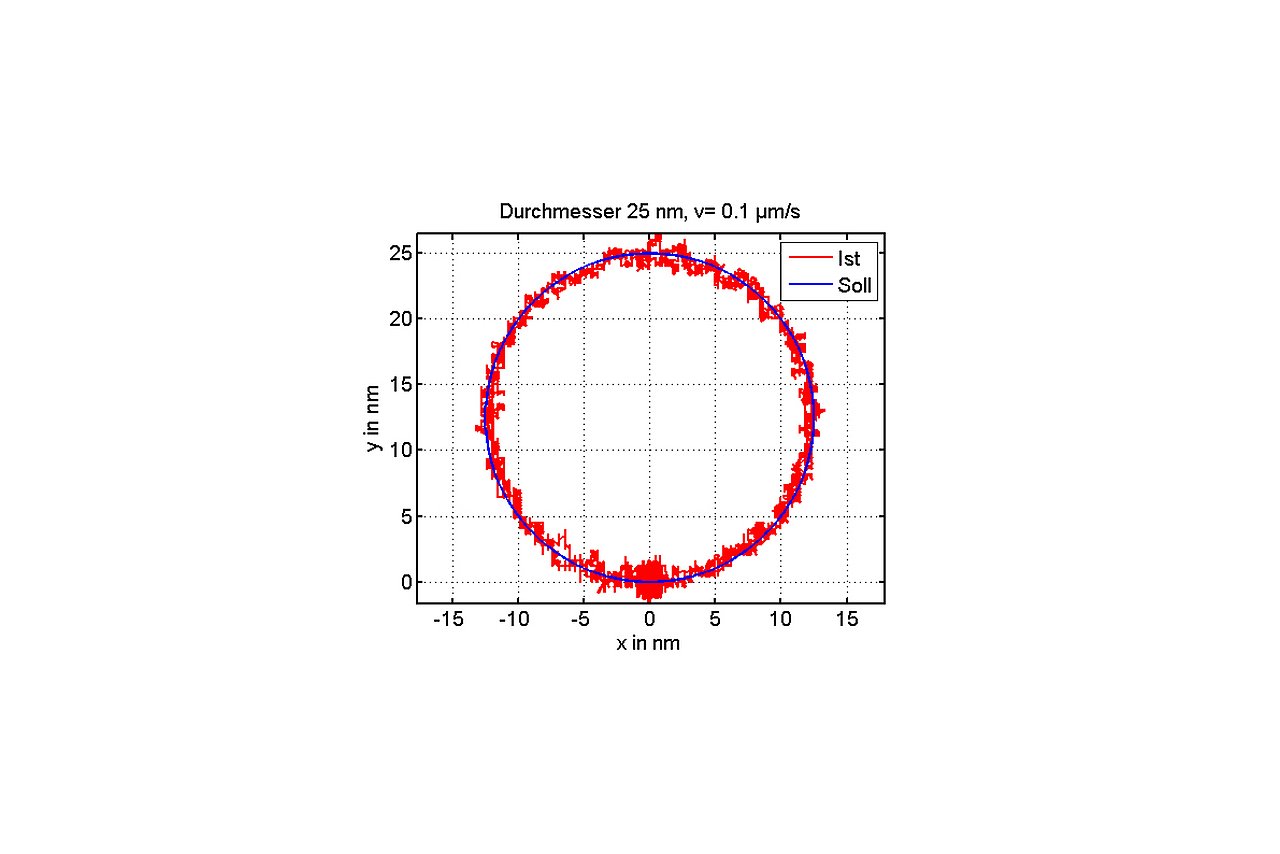
Together with its partners, the Institute has investigated the metrological limits for NPM machines in terms of travel ranges to 450 mm x 450 mm x 80 mm, measurement resolutions to 0.01 nm and reproducibility to <0.3 nm. Furthermore, optimally adapted metrologic solutions for variable application scenarios of NPM machines with different senor and probe systems were developed.
Acronym / Name:
SFB622 / Collaborative Research Centre No. 622 “Nanopositioning and Nanomeasuring Machines”Duration:2002 – 2013
Project website:SFB622
Application:
Research institutions and ultra-precision mechanical engineering|measurement technology| biotechnology| high-precision positioning and motion of objects.Research field:Magnetic 6D-direct drives with nanometre precision
Related content
Vergleich der Scan-Perfomance bei Nanopositioniersystemen mit großem Bewegungsbereich
Stephan Zschäck1. Steffen Hesse2. Avid Amthor1. Michael Katzschmann2. Christoph Schäffel2. Christoph Ament1.tm – Technisches Messen, Oldenbourg Verlag, Band 81, Heft 6, Seiten 335 – 342, ISSN (Online) 2196-7113, ISSN (Print) 0171-8096, DOI: dx.doi.org/10.1515/teme-2014-0358, May 2014
1Technische Universität Ilmenau, Fakultät für Informatik und Automatisierung, Germany, Ilmenau. 2IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ilmenau.Positioning performance of a planar nanopositioning system with 100mm circular travel range
St. Hesse1. C. Schäffel1. M. Katzschmann1. H.-J. Büchner2.27th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Precision Engineering (ASPE), 2012, in Proceedings, ISBN 978-1-887706-61-2, p. 103-106
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ilmenau. 2Technische Universität Ilmenau, Institut für Prozessmess- und Sensortechnik, Ilmenau, Germany.ArticleInterferometric controlled planar positioning system with zerodur slider
S. Hesse1. C. Schäffel1. H-U. Mohr1. H.-J. Büchner2.Ilmenau. In Proceedings. 56. Int. wissenschaftliches Kolloquium der TU Ilmenau. URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2011iwk-103:1
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ilmenau. 2Technische Universität Ilmenau, Institut für Prozessmess- und Sensortechnik.ArticleAuf den Punkt gebracht - Nahezu reibungsfreies Nanopositioniersystem mit großem Verfahrbereich
S. Hesse1.Erschienen in Antriebstechnik - Konstruktion, Entwicklung und Anwendung von Antrieben und Steuerungen, 11/2010
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ilmenau.Article
Contact
Contact
Dr.-Ing. Ludwig Herzog
Head of Mechatronics
ludwig.herzog(at)imms.de+49 (0) 3677 874 93 60
Dr. Ludwig Herzog will provide detail on our research on magnetic 6D direct drives with nm precision for the nm measurement and structuring of objects. He supports you with services for the development of mechatronic systems, for simulation, design and test of MEMS as well as for finite element modelling (FEM) and simulation.
Funding
The project was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) under the reference SFB622.








![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/9/0/csm_20200731_IMG_2732_K4PNP-INPOS_SG_1920x1280_7c70c69f8a.jpg)