Patent DE 10 2020 119 371
Microelectromechanical acceleration sensor
Microelectromechanical sensor systems (MEMS) with comb structures that utilise a capacitive measurement method are used to measure accelerations, particularly from the sensor level. By means of a new type of sensor design, high sensitivity can be achieved on a very small surface area and low susceptibility to errors compared to known designs. The innovative design allows the sensor to be manufactured using a cost-effective standard technology.
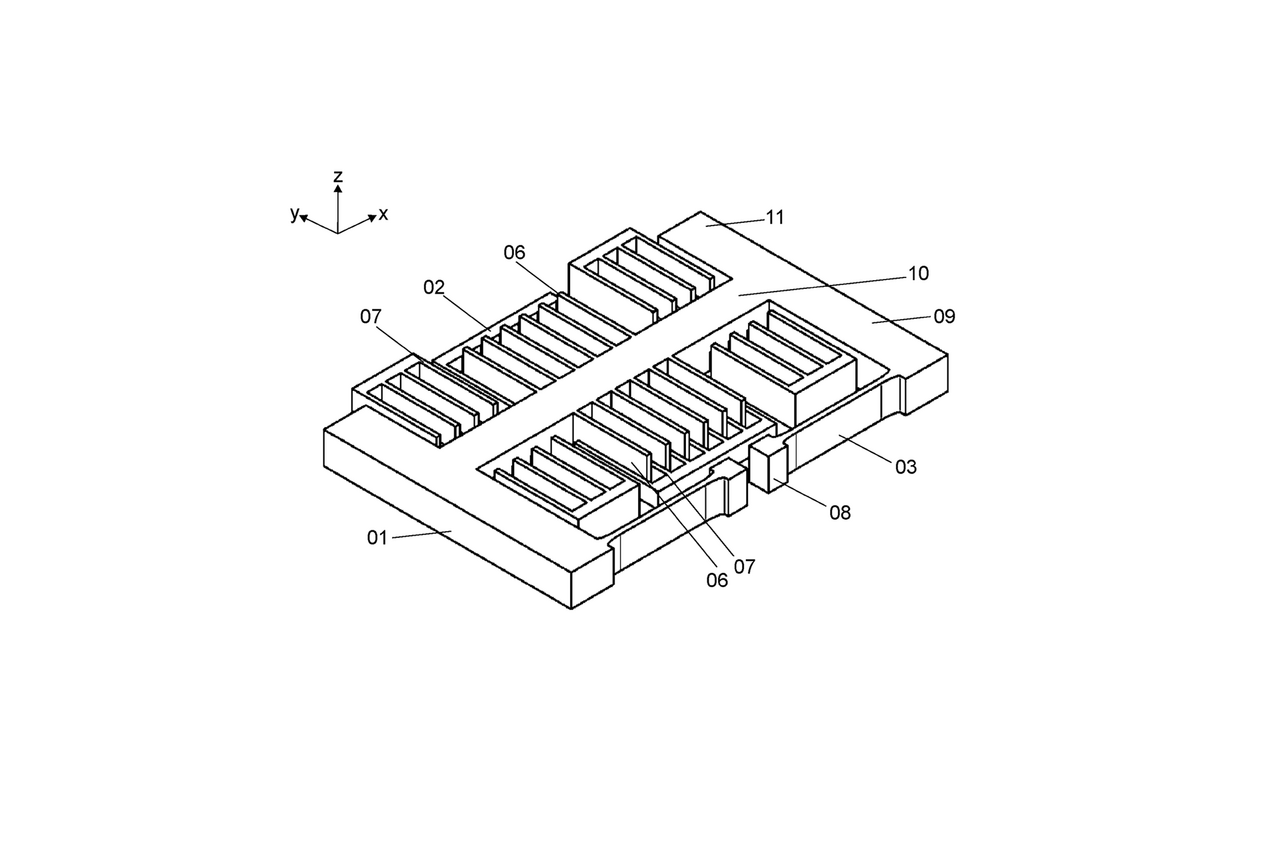
Capacitive MEMS acceleration sensors consist of comb electrodes with interlocking finger structures to minimise the sensor surface. Accelerations are detected by the displacement of a rotor electrode (seismic mass) suspended from a spring relative to a stator electrode. This results in a change in capacitance, which can be analysed electronically either directly or differentially. To detect accelerations vertical to the sensor plane, comb systems with rotor and stator fingers that are partially lowered in height are suitably interconnected. Torsion springs are used to achieve a high sensitivity of the sensor. Known systems of this type are sometimes complex to manufacture, they are prone to errors due to manufacturing tolerances, temperature fluctuations or acceleration forces at the sensor level or do not allow compact integration of additional components or sensors.
The idea behind the invention is a new type of sensor geometry that eliminates the aforementioned disadvantages: The rotor electrode consists of a frame with two parallel lever arms and a centre bar running between the lever arms. The lever arms are each suspended from one of two torsion springs. The centre bar runs parallel to and at a distance from the torsion springs. In this design, the change in capacitance is achieved by changing the area of the opposing electrodes.
Advantages of the invention
- Detection of out-of-plane accelerations with high sensitivity on a small area and with high in-plane stiffness and low susceptibility to errors.
- The design of the acceleration sensor allows the use of cost-efficient MEMS technologies and high-volume production.
- The sensor design enables a space-saving combination with other components or acceleration sensors, e.g. to form a 3D sensor.
- The possibility of manufacturing different sensor designs using the same MEMS technology allows, for example, the optimisation of the seismic mass, the even distribution of the moments occurring at the torsion springs and the reduction of parasitic moments.
Patent No.:DE 10 2020 119 371
Inventor:Steffen Michael
Application:
High-sensitivity chip-sized acceleration sensors (MEMS) | e.g. for the automotive or communications sectorResearch field:Integrated sensor systems
granted patent
Application date:22 July 2020
Date of first publication:05 August 2021
Date of publication of grant:29 April 2021
Related content

Press release,
Hochempfindliche Beschleunigungsmessung mit kleinem MEMS-Sensor
IMMS erhält iENA-Bronzemedaille für mikroelektromechanischen Beschleunigungssensor
Contact
Contact
Dr.-Ing. Ludwig Herzog
Head of Mechatronics
ludwig.herzog(at)imms.de+49 (0) 3677 874 93 60
Dr. Ludwig Herzog will provide detail on our research on magnetic 6D direct drives with nm precision for the nm measurement and structuring of objects. He supports you with services for the development of mechatronic systems, for simulation, design and test of MEMS as well as for finite element modelling (FEM) and simulation.