Patent DE 10 2024 100 703
Method and sensor arrangement for monitoring the function of a machine component
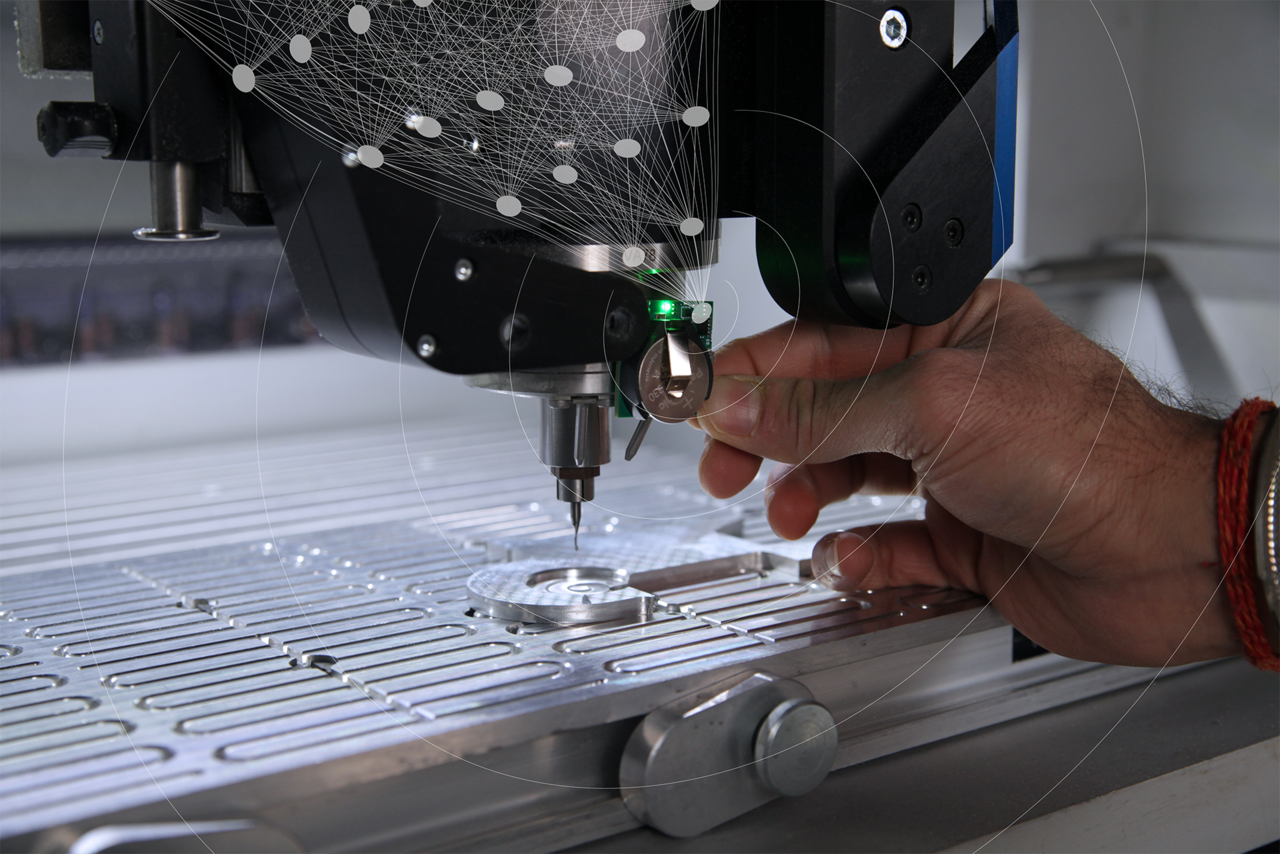
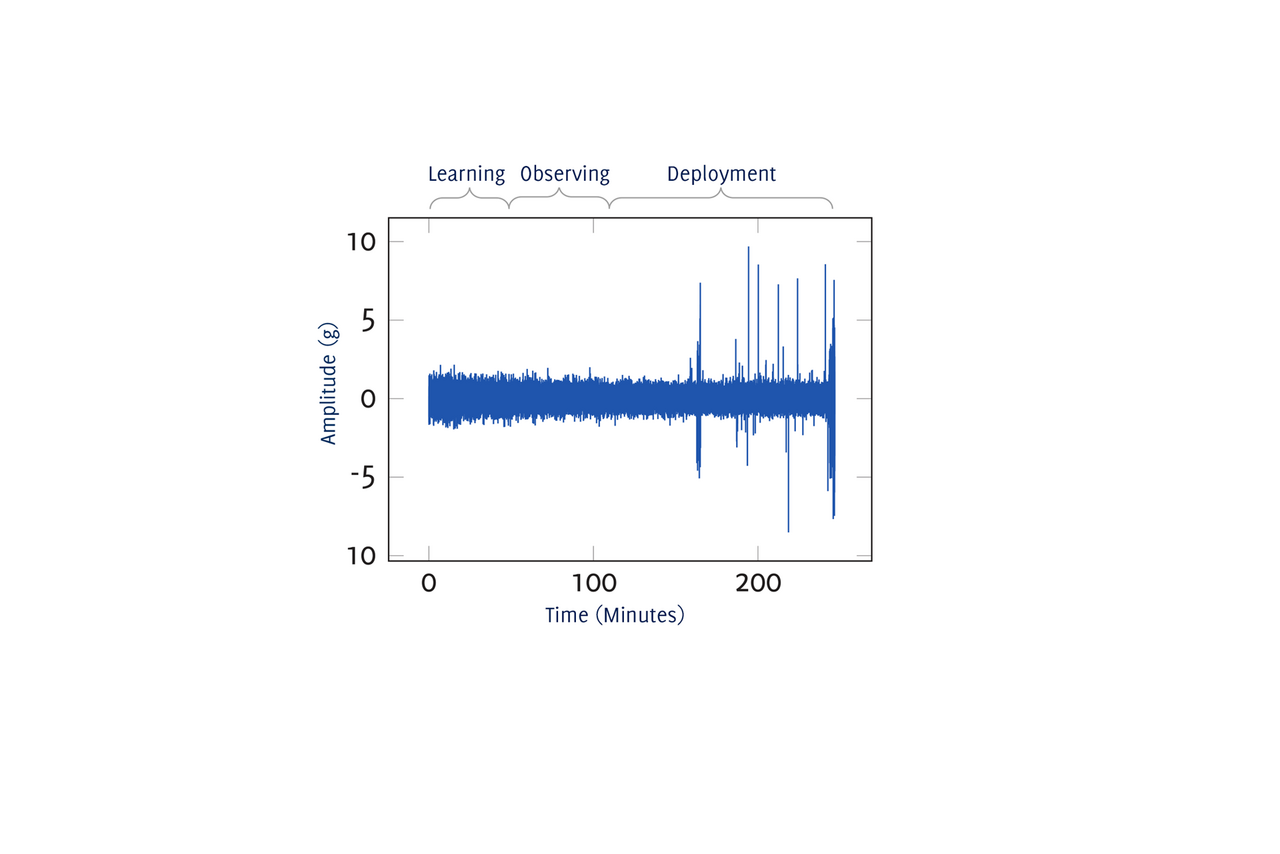
For efficient production processes, it is crucial to detect faults in machines and systems and their components, such as bearings, at an early stage, minimise downtimes and avoid costly repairs. Key concepts in the field of industrial maintenance are therefore condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. Wireless sensors ensure continuous monitoring and condition detection in real time. A new method for data-reduced communication between wireless sensor nodes and monitoring systems makes a major contribution to reducing the energy consumption of wireless sensors, enabling them to be used in numerous locations over many years, even those that are difficult to access.
When monitoring industrial systems, data from wireless sensors is analysed to detect potential problems or deviations from normal operating conditions at an early stage and to predict maintenance requirements. However, continuous real-time monitoring via wireless sensors can have limitations: If the sensors are located in many places or in places that are difficult to access and are expected to work reliably for years, their energy consumption is critical in terms of battery life. The sensors, which are interesting for monitoring, also generate a large amount of data. To date, this can only be transferred to the central monitoring device with a high energy consumption. In addition, defects in machines occur very rarely or not at all during normal operation and certain error states, such as defective bearings and machine parts, cannot be easily triggered.
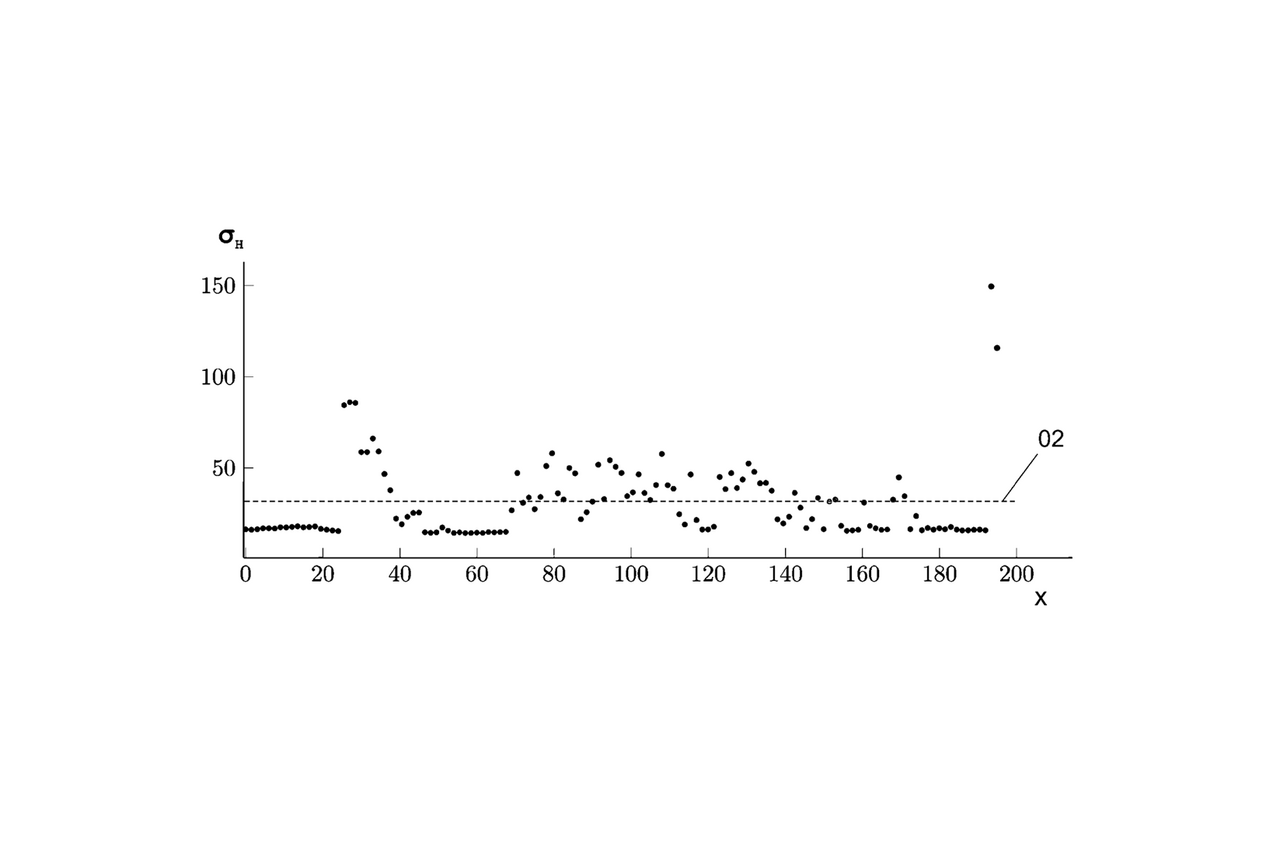
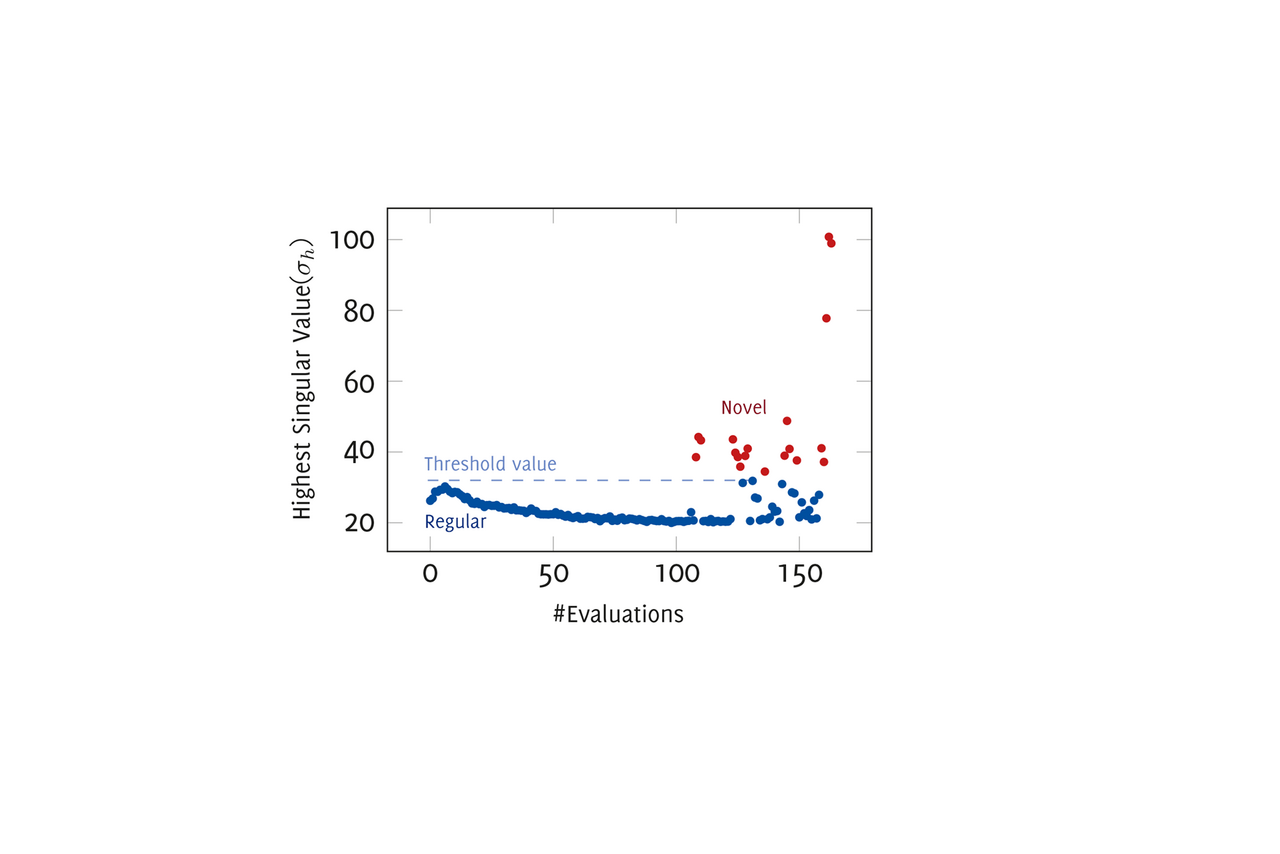
The idea behind the invention is an algorithm that collects data and learns the normal machine behaviour patterns directly on the sensor, largely unsupervised. The regular behaviour patterns of a system and certain novelty criteria, which stand for deviating behaviour, are learned from the recorded data on the wireless sensor. Data is only sent to a central monitoring system if the calculated novelty value deviates from the normal criteria for "healthy behaviour". This completely eliminates the need to transmit raw data to a central monitoring system. This on-device learning and subsequent retraining make the algorithm generalisable for various industrial scenarios and robust against possible data drift. The method for recognising the novelty value of data combines mathematical processes in a specific sequence for ongoing condition monitoring and predictive maintenance over many years.
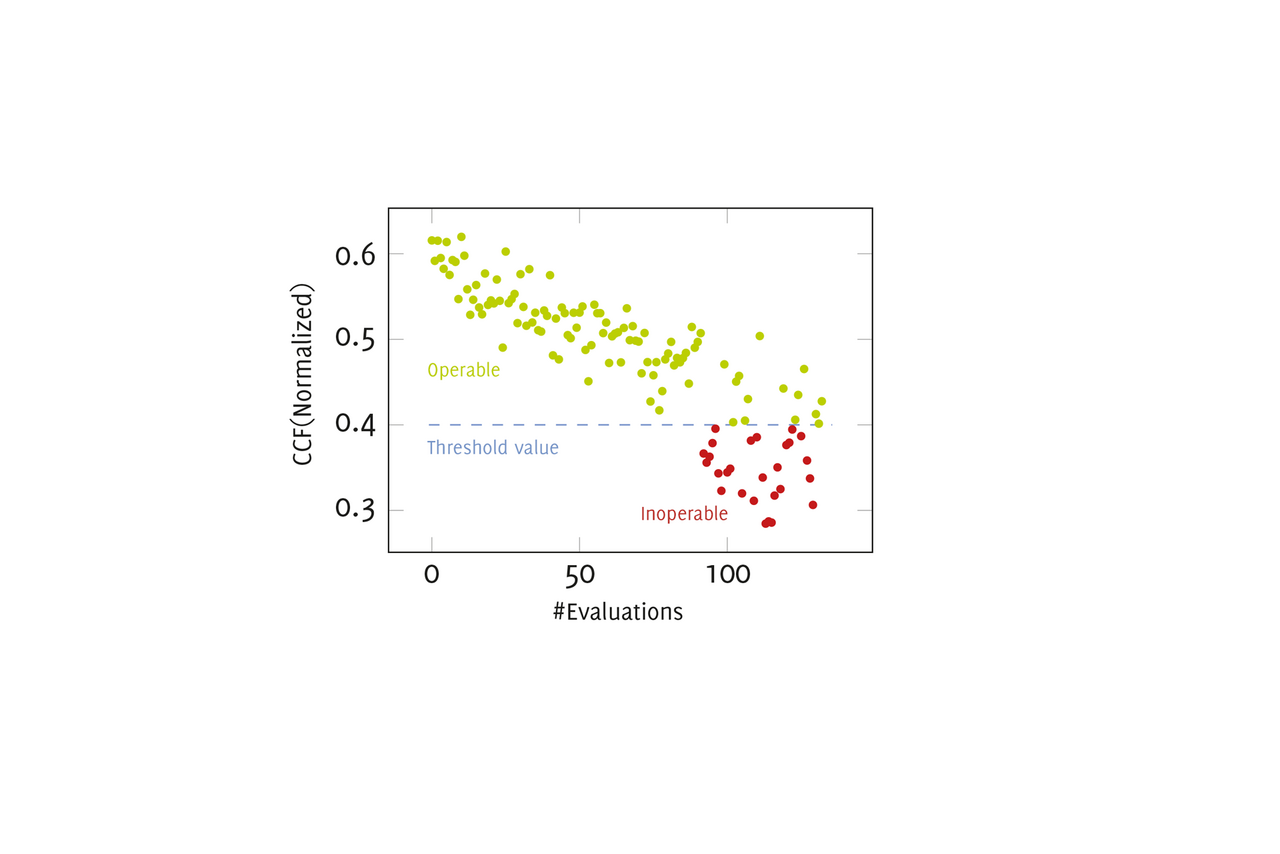
On-device data reduction using singular value decomposition and correlation: In the initialisation phase, the proper operation (good condition) of a bearing, for example, is recorded and a threshold value for detecting irregular conditions is determined by means of automated feature extraction using singular value decomposition. This is further improved in the observation phase by learning certain anomalies and states. By using only the first k dominant singular values and the corresponding parts of the singular value decomposition matrices, a reduced data set is generated on the sensor node for transmission to the monitoring system. In the application phase, a feature vector of newly recorded vibration values is generated. Canonical correlation analysis is used to analyse how different the learned features of the good state are compared to the newly recorded feature and thus qualitatively record changes in state.
Advantages of the invention
- Data processing on the sensor node
- Data reduction in radio transmission
- No need to record fault data and error states in advance
- Reduction in the energy requirements of wireless sensors for increased service life
Patent No.:DE 10 2024 100 703
Inventor:Rick Pandey
Application:
Wireless sensors for industrial maintenance for condition monitoring and predictive maintenanceResearch field:Smart distributed measurement and test systems
granted patent
Application date:11 January 2024
Date of first publication:13 February 2025
Date of publication of grant:13 February 2025
Related content

Project
HoLoDEC
IMMS researches ultra-low-power architectures (ULP) and circuit concepts as well as energy-efficient edge-AI systems with overall system energy modeling
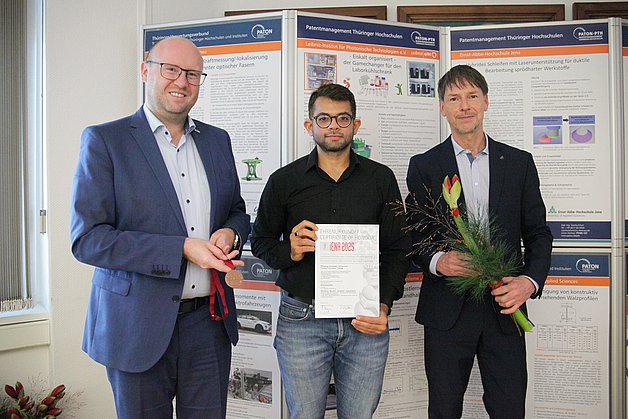

Press release,
Extended service life for self-teaching wireless sensors for industrial maintenance
IMMS patent for edge AI solution wins bronze medal at iENA 2025
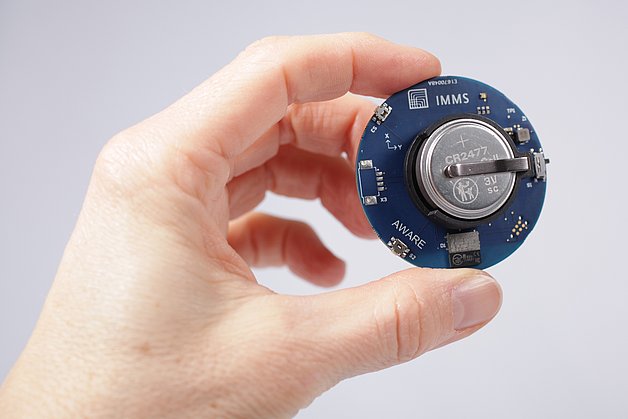
Press release,
AI without the net: Energy-efficient edge AI sensor system for industrial monitoring applications
IMMS exhibits at embedded world
Case Study on Compression of Vibration Data for Distributed Wireless Condition Monitoring Systems.
Rick Pandey1. Felix Grimm2,3. Dominik Nille2. Christoph Böckenhoff2. Jonathan Gamez1. Sebastian Uziel1. Albert Dorneich2. Tino Hutschenreuther1. Silvia Krug1,4.Applied Sciences 2025, 15, 12346. DOI: doi.org/10.3390/app152212346
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ehrenbergstraße 27, 98693 Ilmenau, Germany. 2Balluff GmbH, 73765 Neuhausen auf den Fildern, Germany. 3Institute of Smart Sensors (IIS), University of Stuttgart, 70569 Stuttgart, Germany. 4Department of Computer and Electrical Engineering, Mid Sweden University, Holmgatan 10, 851 70 Sundsvall, Sweden.Smartes Maschinenmonitoring – Anomalien mit Edge-KI detektieren
Sebastian Uziel1.in elektroniknet.de, 11. November, S. 37 - 40, www.elektroniknet.de/automation/industrie-40-iot/anomalien-mit-edge-ki-detektieren.228572.html und in Markt&Technik, Trend Guide 2025, ePaper: wfm-publish.blaetterkatalog.de/frontend/mvc/catalog/by-name/MUT
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ehrenbergstraße 27, 98693 Ilmenau, Germany.Application of the Expert Design Plan Methodology on an Ultra-Low-Power Sensor Frontend
Lorenz Renner1. Ralf Sommer1,2. Yannick Uhlmann3.2025 21th International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods and Applications to Circuit Design (SMACD), July 7 - 10, 2025, Istanbul, Turkiye, pp. 1-4, DOI: doi.org/10.1109/SMACD65553.2025.11092185
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ehrenbergstraße 27, 98693 Ilmenau, Germany. 2Technische Universität Ilmenau, Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, Electronic Circuits and Systems Group, Ilmenau, 98693, Germany. 3Electronics & Drives, Reutlingen University, Reutlingen, Germany.High-Sensitive Demodulator with Built-in Negative Offset Comparator for Passive UHF RFID Tags
Rohit Kesharwani1. Andre Jäger1. Martin Grabmann. Georg Gläser. Eric Schäfer1.IEEE RFID-TA 2024, Forum for advancing RFID technology and practice, Daytona Beach, FL, USA, December 18–20, 2024
1IMMS Institut für Mikroelektronik- und Mechatronik-Systeme gemeinnützige GmbH, Ehrenbergstraße 27, 98693 Ilmenau, Germany.

Event,
SMACD 2025
International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods, and Applications to Circuit Design

Event,
InnoCON 2025
Innovation policy flagship event of the German Land of Thüringen. Topic “Key technologies: Paving the way for the world of tomorrow“
Contact
Contact
Dr.-Ing. Tino Hutschenreuther
Head of System Design
tino.hutschenreuther(at)imms.de+49 (0) 3677 874 93 40
Dr. Tino Hutschenreuther will answer your questions on our research in Smart distributed measurement and test systems and the related core topics Analysis of distributed IoT systems, Embedded AI and Real-time data processing and communications, on the lead applications Adaptive edge AI systems for industrial application and IoT systems for cooperative environmental monitoring as well as on the range of services for the development of embedded systems.